Viruses, Viroids, Prions and Lichens
Akanksha Soni, Academic Content Writer at Edumarz
- Viruses:-
- In Whitaker’s classification of the five kingdoms, there is no mention of acellular organisms such as lichens, viruses, viroids, and prions.
- When we fall ill like a cold or flu, it is due to a virus.
- Viruses mean botulism or poisonous fluid.
- Viruses do not find a place in kingdom classification since they are not truly ‘living’. Living organisms are those that have a cellular structure.
- The viruses are acellular organisms characterized by an inert crystalline structure outside the living cell. Once they infect a cell they take over the host cell’s machinery to replicate themselves, leading to the death of the host.
- Viruses are obligate parasites. They cannot complete their life cycle without a suitable host.
- Viruses contain genetic material which can be either DNA or RNA, both genetic materials may not contain any virus.
Fig:- Viruses
Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV):-
- It was discovered by Dmitri Ivanowsky (1892) in the mosaic disease of tobacco. They are discovered to be smaller than bacteria because they pass through bacteria-proof filters. M.W. Beijerinek (1898) proved that extracts from infected tobacco plants could cause infection in healthy plants and named the new pathogen “virus” and called the fluid was called Contagium vivum fluidum.
- W.M. Stanley (1935) demonstrated that viruses can be crystallized and that crystals largely consist of proteins. They are inactive outside their specific host cell.
- TMV is a single stranded RNA. It particularly affects tobacco plants and other members of the family Solanaceae.
- Viruses that infect the bacteria are called Bacterial viruses or bacteriophages. These are generally double-stranded DNA viruses.
- Capsomeres are small subunits of the capsid protein coat that protect the nucleic acid. These capsomeres are geometrically arranged in helical or polyhedral patterns.
- Viruses cause diseases such as mumps, smallpox, herpes, AIDS, and influenza. Mosaic formation, leaf rolling and curling, yellowing and vein clearing, dwarfing, and stunted growth can all be symptoms in plants.
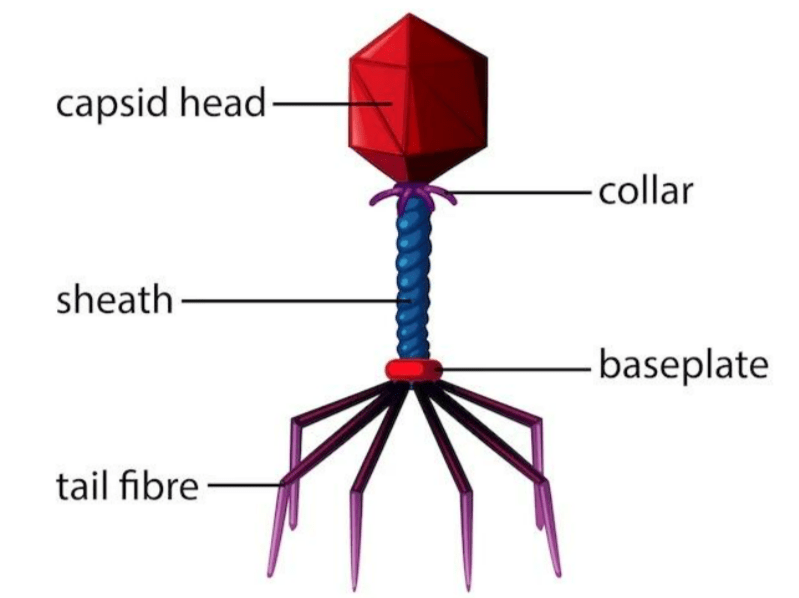
Fig:- Bacteriophage
1. Viroids:-
- Viroids were discovered by T.O. Diener.
- Viroids is a new infectious agent that was smaller than a virus and caused potato spindle tuber disease.
- It was discovered to be a free RNA lacking the protein coat found in viruses, thus the name viroid.
- The molecular weight of viroid RNA was low..
2. Prions:-
- In modern medicine, some infectious neurological diseases are transmitted by an agent containing abnormally folded protein. The agent was similar in shape to a virus. These agents were called prions. The most notable diseases caused by prions are bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) commonly known as mad cow disease in cattle and Cr–Jacob disease (CJD) in humans.
3. Lichens:-
- Lichens are symbiotic associations or mutualism.
- Algae and fungi have a mutually beneficial relationship. The algal component is referred to as phycobiont, and the fungal component is referred to as mycobiont; both are autotrophic and heterotrophic. Fungi require algae for food, and algae require fungi for shelter and the absorption of minerals, nutrients, and water.
- Lichens are good pollution indicators. Lichens do not thrive in polluted environments.


