Suminder kaur, Academic Content Writer at Edumarz
Ecosystem- It is a structural and functional unit of the biosphere consisting of living organisms and their interaction with food chain and biogeochemical cycles. For example ponds, forests, etc.
For instance, let’s take an example of a garden that has a diverse range of flora, including grasses, trees, flowering and non-flowering plants, as well as creatures such as frogs and insects. Here, these organisms are interacting with one other as well as abiotic conditions that impact their development, reproduction, and other activities.
Ecosystems are of two types – Natural ecosystem and artificial ecosystem.
NATURAL ECOSYSTEM – Natural Ecosystem refers to the ecosystem that exists in nature. Forests, grasslands, deserts, ponds, lakes, rivers, estuaries, and the sea are examples of natural ecosystems.
ARTIFICIAL ECOSYSTEM – Artificial Environment is a term used to describe a man-made ecosystem. For example, a garden, crop field, aquarium, etc.
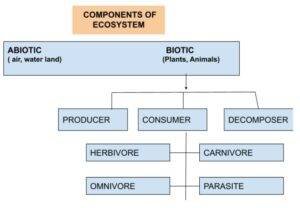
Abiotic factors: It includes all the non- living factors such as air, water, temperature, rain, soil,pH, minerals, etc.
Biotic factors include all the living factors such as plants, animals and microorganisms.
We further subdivide biotic components on the basis of mode of nutrition into three categories such as producers, consumers and decomposers.
Plants, blue green algae, are producers who can manufacture their own food.
Consumers are those who directly or indirectly depend on producers for their nutrition. For example, animals, humans, etc.
Decomposers are those organisms who feed on dead and decay organisms. For example, fungi.
Division of consumers
Carnivores are creatures that consume meat. Example, lion, tiger
Herbivores are plant eaters . eg goat, deer.
Plants and animals both are consumed by omnivores.
Parasites dwell inside their hosts and rely on them for survival.