Suminder kaur, Academic Content Writer at Edumarz
FOOD CHAIN
- It’s the process of eating and being eaten, or, to put it another way, one creature consumes another organism, which is then devoured by another organism.
- Producers, consumers, and decomposers make up the majority of a food chain.
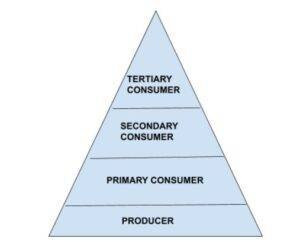
- The trophic level at which energy is transferred is referred to as each stage of the food chain. Because energy availability is essentially non-existent at 4-5 trophic levels, a food chain usually has just 3-4 trophic levels. The food chains are shown as pyramids, with various creatures occupying different levels, as shown:
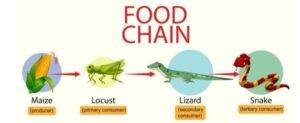
- Examples of food chains:
- Terrestrial Food Chain
(a) Green Plants → Deer → Lion
(b) Grass → locust → Frog → Snake → Hawk
- For example: Aquatic Food Chain
(c) water Plants → Zooplankton → Small Fish → Large Fish
FLOW OF ENERGY IN FOOD CHAIN
- It is unidirectional.
- Only 1% of sunlight energy is captured by green plants to convert it into food energy.
- In the field of energy transmission, Raymond Lindeman’s 10% law is observed. “Only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to another trophic level,” according to this regulation. The remaining 90% will be consumed in various processes by the current trophic level. As a result, trophic levels are usually three to four in a food chain.
- Decrease in energy.
1KJ -> 10 KJ -> 100 KJ -> 1000KJ.
- BIOLOGICAL MAGNIFICATION : Harmful chemical concentration increases in subsequent trophic levels in a food chain. This is called biological magnification.
- As a result of this process, the organisms at higher trophic level will get a high amount of harmful chemicals. For example humans.
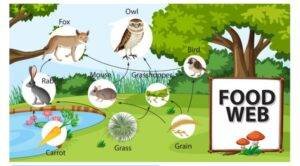
FOOD WEB
- The term “Food Web” refers to the interconnection of food chains. It demonstrates the interdependence of the food chain.
CHARACTERISTICS OF FOOD WEB
- Food webs are never straight since they are produced by the interconnection of food chains.
- The food network provides alternate food supply routes. If a certain species goes extinct, the predator can prey on another species.
- Ecosystem stability is improved via food webs.